All You Need to Know About Data Analytics
Data Analytics has emerged as one of the most in-demand careers in recent years. This in-depth article covers the applications of DA, skills to become an analyst, career scope, and more.
Data Analytics has emerged as one of the most in-demand careers in recent years. Learn the nitty-gritty of Data Analytics and pave the way for a successful career.
Learn about the applications of DA, skills to become an analyst, career scope, and more. Let’s dive in!
“Data is the new oil” - You must have heard this quote a good number of times, and it’s true indeed. Just the way oil propelled the industrial revolution, data has been at the forefront of modern industry. Just the way oil can be transformed into more constructive elements that increase its value, data will have a much higher value when it is processed, analyzed, and utilized properly.
Enter - Data Analytics
If data is the new oil, analytics would be the refinery.
Analytics is simply the process of making sense of the quintillions of unstructured data (also termed ‘Big Data’) to generate more value out of it and make better business and social decisions.
Data analytics is making quite the buzz in the job sector with companies rolling out vacancies, and students flocking to pursue a career in analytics.
And rightly so! Data analytics is a keystone in almost all business operations today, from sales and marketing to product and customer retention.
But why is it so important for companies and why is it being deemed as one of the brightest careers? Let's jump right into the devil of the details and learn more about data analytics.
Table of contents-
Real-world examples of data analytics
Skills to become a data analyst
Career scope in data analytics
Data analytics vs Data Science
What is Data Analytics?
As the name suggests, it's about studying and analyzing data to figure out hidden trends and patterns that help businesses make better decisions.
Want more clarity?
Let's say McDonald's sold 10 million burgers in India in 2021.
They want to analyze purchase patterns so that they can come up with ideas to sell more, or make more revenue. In that case, one of the things they'd do is to evaluate and understand the purchase behaviours - Age, gender, location, etc. Now the data analysts get to work and they find out that 70% of individuals in the age group (18-30) bought from McDonald's again, while only 10% of people in the age group (30-50) were retained.
Deriving this data from a group of 100 customers could be done manually but when it comes to Big Data (datasets that are too complex for traditional processors), we need data analytics.
Based on these trends, McDonald's will make decisions - on whether to amplify its focus on the (18-30) target market or to bring a product that caters to the (30-50) age group.
Similarly, thousands of companies use analytics to bring out insights and predictability to make better business decisions.
It's no news that we live in a world full of data captured through the various devices and channels we use daily. A 2021 report by Statista witnessed 79 zettabytes of data generated throughout the world. This amount is only going to double by 2025.
As all of this data is raw and unstructured, we can't just let it all get lost in the ocean. We need to make sense of it and produce meaningful patterns and outcomes that will help companies make better decisions and ease the process for customers.
Who are data analysts?

Data analysts are professionals with the skills to turn raw and unstructured data into useful information and stories that businesses can use for critical decision-making.
Even though most of the extraction process is automated, data analysts are responsible for defining the subsets, removing corrupted data, fixing coding errors, developing and maintaining databases for storage, converting them into a readable format, and performing analysis for the qualitative assessment of data.
They are adept at using automated and statistical tools to identify trends and behaviours within huge datasets.
Analysts find answers to pertinent questions like-
- What's the target market for a company?
- What age group needs a particular service the most?
- What set of people are most susceptible to a particular disease?
- What's the next update or product that customers can benefit from?
These people are in demand in several industries including government, medicine, business, finance, criminal justice, logistics, software, and more.
This means there's no shortage of opportunities for someone who is aspiring to become a data analyst.
With that being said, let's look at a few examples of how big companies are using big data and analytics to drive change-
Real-world Examples of Data Analytics
Tesla - Along with revolutionizing electric vehicles, this brainchild of the eccentric billionaire Elon Musk has placed itself as the leader of the self-driving car market. We're anticipating a fully autonomous, driverless future.
But how does that work?
You guessed it right - Data Analytics. These automatic vehicles process vision, sound, and radar data using a neural net. Cars share data when they pass each other which is then analyzed to decide the correct path, traffic, and other things.
This is a perfect example of IoT analytics. IoT refers to the network of physical objects that uses sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices over the internet. (Learn IoT in detail)
We're looking at a fleet of automated vehicles sharing real-world insights to improve our experience.
Amazon and other E-commerce websites - From you liking a particular product, searching for it, adding it to a cart, or even just giving it a simple glance, every activity is tracked and stored in the database. Next, Amazon uses this data to know what you need or want and recommends the same or similar products from their huge inventory.
This is the way the company earns almost 35% of its annual sales - through product recommendations.
However, it's not one-way traffic as it also improves customers' experience by making their search more relevant and easier.
Uber Eats - From being a leader in the taxi business, Uber decided to expand to the food delivery market with 'Uber Eats' and boy! How well they have done it.
They based their mission around ''delivering food when it's still warm'' and they have been sticking to their mission with the help of big data and analytics.
To make it work, they collect the data on the time taken to prepare a certain food item, so they can precisely assign the pick-up time to the delivery person. It allows the riders to pick up more meals on the way and carry more than one meal per trip to serve more customers in less time.
In fact, they have also hired meteorologists to predict the weather conditions based on data and how they might affect the delivery.
(You'll find more real-world applications of data analytics in this article)
Distinguishing Data Science from Data Analytics
Difference 1: Approaches to Data Handling
Data scientists and data analysts differ in two primary ways: their data processing methods and the outcomes they generate.
Data analysts focus on addressing specific, pre-identified organizational issues. They sift through extensive datasets to uncover trends and patterns and use visualizations like graphs and charts to present their findings. These visual representations aid key stakeholders in making data-driven strategic decisions.
In contrast, data scientists ponder the questions a business should ask or may want to explore. They create innovative data modeling techniques, software programs, mathematical prediction models, and individualized analyses. For instance, they might construct a machine capable of automating tasks based on data and continually refine it as new patterns emerge.
Difference 2: Tools and Skills
Another key distinction lies in the tools and skills required for each role. Data analysts are typically proficient in software like Excel, and, in some cases, programming and backend languages such as Python, R, SAS, and SQL. These technologies and languages are essential for tasks such as data mining, statistical analysis, database management, and reporting.
In contrast, data scientists need expertise in software development, data mining, and programming languages like Java, AI, and OD programming.
Difference 3: Scope of Analysis
Data analysts primarily focus on historical data and the present state of affairs within an organization. They use data to provide insights into current business performance, customer behavior, and operational efficiency. Their analyses are typically retrospective and geared toward improving ongoing processes.
On the other hand, data scientists often engage in predictive and prescriptive analytics. They not only analyze historical data but also develop models that can forecast future trends and prescribe actions for optimizing outcomes. Data scientists are more forward-looking and may design algorithms that can be applied for strategic planning and long-term decision-making.
Difference 4: Complexity of Problem-Solving
Data analysts typically address well-defined, structured problems that are already known to the organization. They work on specific, straightforward inquiries related to business metrics, customer preferences, or operational efficiency. Their problem-solving tends to be within established frameworks.
Data scientists, conversely, tackle complex, unstructured problems that may not have clear solutions. They explore novel questions and often deal with messy, unorganized data. Their problem-solving requires creativity, algorithm development, and the ability to devise innovative approaches to extract valuable insights from chaotic datasets.
The Significance of Data Analytics
The success and growth of a company often hinge on effective data analytics. It empowers businesses to make informed decisions about their operations' direction. By analyzing historical data and identifying trends, businesses can strategically plan, reliably predict, and swiftly respond to a dynamic market, gaining a competitive edge.
Data analytics can lead to cost savings and increased return on investment (ROI) by pinpointing bottlenecks, streamlining processes, and optimizing resource allocation. It also has the potential to detect fraud or wastage.
Can recent graduates work as Data Analysts?
Yes, recent graduates with the requisite degrees and analytical skills can begin their careers as entry-level data analysts. Their prospects of securing a data analyst position can be enhanced by gaining experience through internships, projects, or certifications.
Skills needed to become a Data Analyst
By now you'd have realized the importance of Data analytics. The important question is - How to become a data analyst? What skills should you acquire and what tools do you need to be adept with?

Coding Languages
Python - If you're an aspiring analyst, learning Python should be your top priority. It is a general-purpose programming language with a good number of specialized libraries that cater to Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Owing to these attributes, Python ranked number one in IEEE'S spectrum 2019 survey. In the increasing AI landscape, analysts need to be efficient in Python.
R language - R programming language's syntax and structure were built to support analytics. It can handle large buckets of data and that's the reason it is best suited for several businesses. And precisely why it should be a top priority for analysts.
Database languages
SQL - To analyze data, you need to be proficient in database languages; the first and foremost of which is - Structured Query Language or SQL.
Almost every organization needs people with experience in SQL. It is used to store and manage data, relate multiple databases (like the ones used by E-com websites to recommend products), or build new database structures.
SQL is simply the advanced version of Excel; in a way, it can work on huge datasets which is not possible with Excel.
An SQL developer has a high demand across the world and if you want to work with big data, SQL should be one of the first items on your plate.
NoSQL - As the name suggests, NoSQL can structure the data in any way and there's no standard NoSQL framework. Every data analyst should build their aptitude with NoSQL databases. To learn NoSQL you can start with a framework like MongoDB.
Data Visualization & Data Cleaning
So, you've churned out the conclusive data and drawn insights, now what?
Now you need to explain those insights to the stakeholders who might not be trained in data analysis. This is where you use visualization to present the key findings with the help of graphics, pie charts, or other illustrations.
This skill enables you to communicate valuable insights to the company leaders and shape future decisions.
Undoubtedly, it's an important skill to learn as the better stories you can tell from the given chunk of data, the better decisions your company is going to make. Analysts need to be able to look at data from different perspectives and dig for more insights.
Data Cleaning is an integral part of analytics, as with a cleaned dataset even simple algorithms can derive great insights. As tech writer Ajay Sarangam mentions-
"Most data scientists spend around 80% of time cleaning data. Why? Because of a simple truth in ML; Better data beats fancier algorithms."
On the tail's side, uncleaned data can generate misleading trends and can lead to bad decision-making for companies.
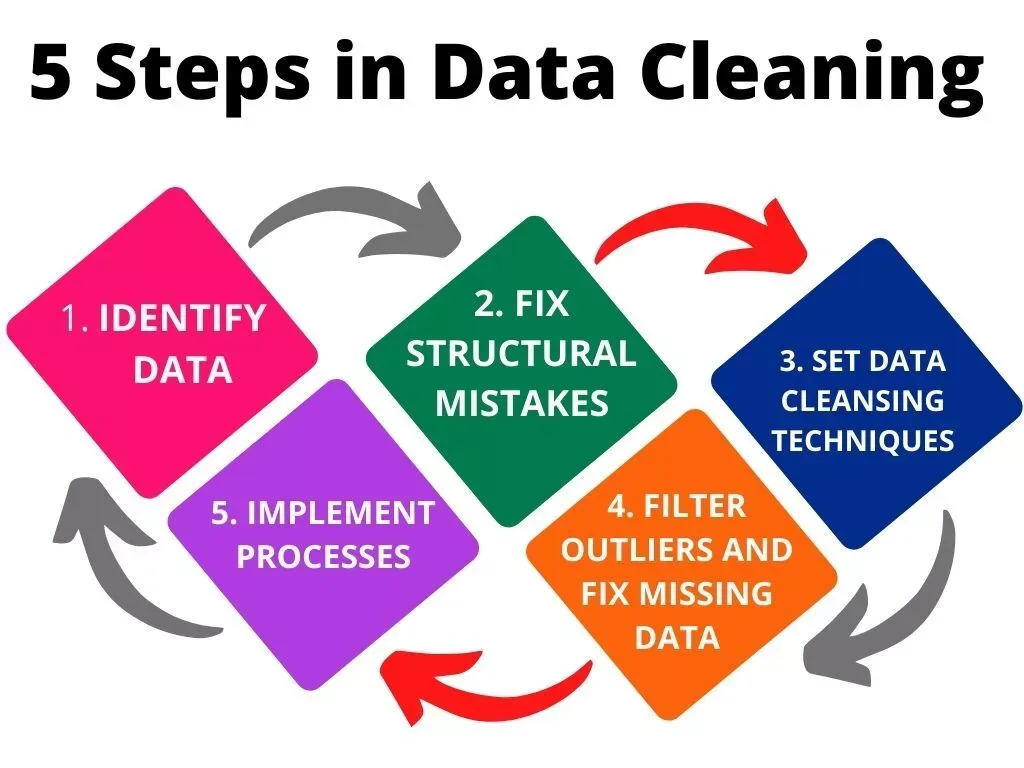
It's no hyperbole that companies would want someone who can rut through and clean the data before running algorithms.
Mathematical Skills
Having mathematical skills is non-negotiable in the field of data analytics.
Analysts need to have good knowledge of linear algebra, calculus, statistics, and probability to make sense of data.
Where algebra has uses in machine learning, we need calculus to build the objective functions for algorithms.
Probability and statistics are quite obvious as they match the description of a data analyst's role - collecting, analyzing, predicting, and presenting data.
If you have a good hold of probability and statistics you'll more likely be able to -
- Find patterns and trends in data
- Make predictions based on the data
- Avoid logical errors from your analysis
Microsoft Excel
This Microsoft spreadsheet is used by more than 750 million users on the planet. It's one of the most common skills in all kinds of job postings.
However, calling it just a spreadsheet would be an understatement.
Excel has good analysis power under its hood. It comes with its own programming language called VBA that can save people a lot of time on frequently-implemented, repetitive projects like finance, payroll, accounting, etc.
Even if analysts work with more advanced tools like SQL, Excel will always be a primary requirement.
Critical thinking
To extract useful insights from a chunk of data, you need to ask the right questions and identify patterns. You need to be able to go above and beyond basic parameters and think from different perspectives. As a data analyst, you'll be unfurling and synthesizing connections that are not clearly visible.
Though there's no defined way to hone your critical thinking skills, you can always start by asking questions that arise from a dataset.
- What are the accomplishments indicated by the data?
- What loopholes are coming out from it?
- What's the meaning behind a specific pattern?
Practicing these basic questions consistently and evaluating the existing evidence will certainly boost your critical thinking.
Presentation Skills
Even if you're a pro at data visualization, you'll need good presentation skills to put your points forth. If you're not engaging during a presentation, you won't be able to draw the board's attention.
Like all other soft skills, you can get better at presentation with practice. Remember that even expert presenters can get nervous at times, so you don't need to panic if you don't get it right the first few times.
Here's an insightful article from Forbes to get better at presenting
Career Scope for Data Analysts
There has never been a better time to be a data analyst professional. With about 2.5 quintillion bytes of data created every day, the demand for people who can help companies leverage that data is inevitable. There are 65,000+ data analyst job openings in India at present, according to LinkedIn.
And this demand is indicated by the increase in their salary in recent times.
According to Glassdoor, the median salary for a data professional in India is INR 5,30,000 /year and as the recent trends suggest - it's only going to go up north.
Apart from the increased demand and salary, analysts get to contribute to the decision-making process at the highest level. This can also open doors for more managerial positions.
Data analytics has applications in numerous industries today including IT, finance, media, E-commerce, outsourcing companies, etc.
Top companies that hire data analysts are - Accenture, TCS, Google, Amazon, Capgemini, IBM, and Deloitte to name a few.
It can also solve many concerns with data security. For example - MasterCard companies use analytics to get rid of fake account activities.
Another notable sector that is reliant on data analytics is - the Internet of things (IoT). IoT is a fast-growing sector that includes autonomous vehicles, traffic management, environmental monitoring, smart cities, and homes, etc.
Acccording to Statista, we already have an estimated 30.73 billion IOT-connected devices. Data analytics allow IoT applications to manage the volume and structure of huge datasets effectively.
As the future of IoT is limitless (we even have smart clothes and smart shoes now), so is the need for data analytics.
All factors point to one thing - A career in Data analytics has great potential and if you're willing to get into the nitty-gritty of analyzing data, you shouldn't miss out on this ocean of opportunities.
Data Analytics vs Data Science
Companies across the world have different ways to define job roles. And it does create confusion among the masses between the specific job role and the required skills.
A primary example of this would be the distinction between - A data analyst and a data scientist. Both represent two of the most in-demand jobs in the current scenario. While both analysts and data scientists work with data, they require different skills and responsibilities.
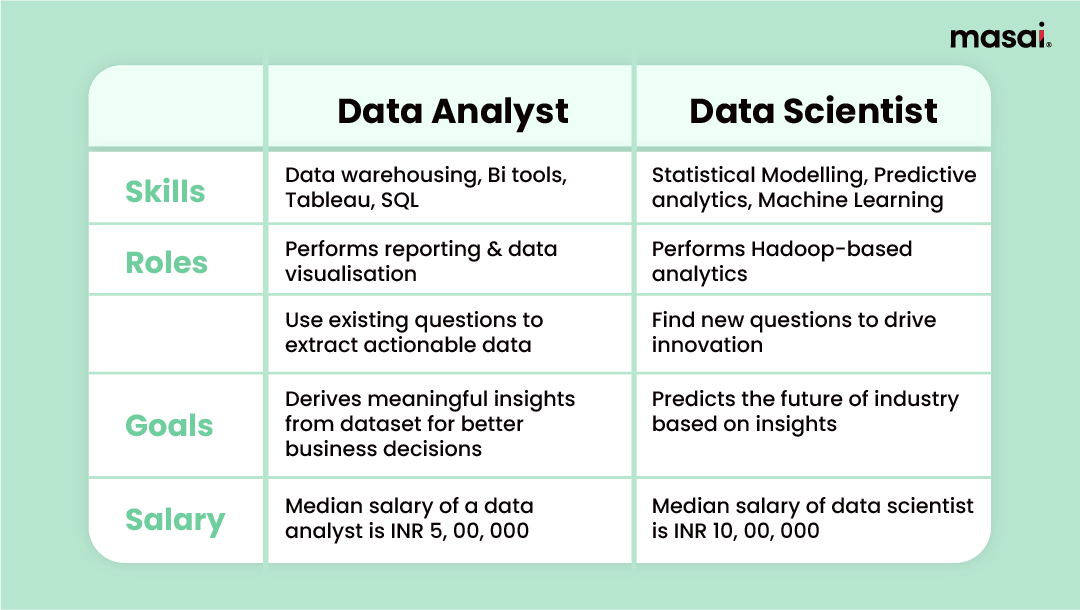
Let's look at a few major differences -
- While a data analyst derives meaningful patterns and insights from a dataset, a data scientist can predict the future based on past derivations.
- A data scientist examines data from multiple disconnected sources. On the other hand, a data analyst generally extracts data from a single source.
- In most cases, a data analyst doesn't need machine learning experience whereas a data scientist needs to be well-versed with machine learning and building statistical models.
- A data analyst generally finds answers to the questions that are needed by the business while a data scientist conceptualizes and forms questions on their own that have the potential to make long-term plans for the business.
- A data analyst uses data visualization tools like Power BI, Tableau, MS Excel, etc. to glean meaningful insights. A data scientist runs casualty experiments by applying A/B experiments to identify the root issues of a result.
Conclusion
In the previous section, we saw the key differences between analytics and data science. Both of these branches function on big data.
A data scientist generally has all the skills possessed by an analyst in addition to a few other skills.
However, if you're willing to get into big data, data analytics is the perfect launchpad for you. After getting some experience in analytics, you can swiftly transition to data science once you add advanced machine learning and predictive analytics skills to your repertoire.
And, to skill students in the field of analytics, Masai provides a part-time Data Analytics course at zero upfront fee. You'll receive training in all the tools and languages that are needed in a professional business analyst including MS-Excel, Python, SQL, Tableau, Probability & Statistics, and Machine learning in this 30-week course.
Take the first step, check out this course, and do a qualitative analysis (that's what you have set out to do, anyway) before making a decision.
Cheers!
Other Important Resources:
5 real-world examples of data analytics

