What is Prompt Engineering?
Learn everything about prompt engineering, types of prompts, how you can engineer your prompts to create your desired outputs, and what skills you need to become a prompt engineer.

Introduction
Prompt engineering, in simple terms, is feeding carefully ideated inputs to AI models to generate optimal output that will be much more useful, effective, and accurate.
I was in the third standard when I used to pronounce ‘island’ as ‘eezland’. We all have been there! By the time I reached eighth grade, I was awarded the ‘Most creative storyteller’ certificate.
The irony, right? That shows 2 things. First, I have come a long way from struggling to pronounce a basic word to being a professional writer. Second, I understood the importance of feeding myself good inputs to produce good outputs.
How? It was evident how I struggled with English as a language. In those 5 years, from class 3 to 8, I don't know how many English TV series I watched, how many Jim Corbett books I read, and how many riddles I solved!!
Without even realizing it, I gradually began to become better at English. Plot twists and mystery drama were always at the top of my head, and critical thinking became my new unpursued hobby.
And that's how I clinched the 'Most Creative Storyteller' certificate. I am trying to say that your inputs are the base of your outputs. Prompt engineering is no different!
Let's dive deep into the topic and understand prompt engineering and how you can become a prompt engineer.
What is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt Engineering is no rocket science. It's a technical term for providing input (prompting/requesting) via text to an AI tool to obtain a specific and desirable output (answer).
Now, let's imagine a specific scenario. Let's say I told you to make pasta. Now, you will need a really good sauce. A sauce bought from a local market does the job, but what if you source your tomato and basil levels directly from a farmer and make it at home? Chances are it will taste a lot better.
What if you directly source the other fresh ingredients from a farmer's field? It will unlock a stunning epitome of delicious savoury!
Like better ingredients can produce better food, better prompts can produce better outputs. The art of writing these prompts is called prompt engineering.
Strong prompt engineering requires you to provide a detailed context of your desired output and refine your prompts meticulously to achieve your specific and useful result.

Prompt Engineering & Generative AI
Whether you want to tell ChatGPT to rewrite an ATS-friendly resume or create a content calendar, anyone can be a prompt engineer!
Generative AI models can generate text, images, video, and more. Anyone can do prompt engineering using natural language as inputs like ChatGPT or DALL-E. AI engineers use prompt engineering when training or refining LLMs (Large Language Models) using very specific prompts.
For instance, if you are using GPT to, let's say, create a creative meme copy for your brand, you can begin by giving a very basic prompt: 'Give me a few short and concise meme content pointers for a clothing brand'.
As this prompt is very vague and the context is not clear, like the tonality and style, brand voice, etc., you might end up adding context like 'make it funnier', 'should be relevant to the clothing industry', 'it should be related to organic clothing', etc.
To avoid this chain of prompts, prompt engineering focuses on creating a comprehensive prompt that sets the context for the desired output. As a result, the produced output will be much more favourable and accurate.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI, or Gen AI, as people call it lovingly, is a subset of artificial intelligence that can create new types of content, including text, images, code, audio, and video.
Unlike traditional AI models, which used to primarily focus on classification, prediction, or recognition (subsets of Machine Learning algorithms), Generative AI is trained on large sets of data.
So, when you ask ChatGPT to write a piece of code or ask DALL-E to produce an image, they leverage their learning patterns on what they have been trained upon and produce original creative outputs that resemble human-generated content.
During training, these AI models identify and learn patterns, structures, and relationships within the data. After successful training, these models can create new content based on their learning.
For example, text-based models like GPT can answer questions, draft emails, or even generate code snippets. Image-based models like DALL-E can design original high-end graphics and art from scratch.
Use of Prompt Engineering in Generative AI
Prompt Engineering has become crucial for AI engineers to create and deliver better solutions, such as AI chatbots that can manage customer queries or provide quick logistics support and resolution. This has proven to be extremely efficient, without much human intervention.
Making sure that Generative AI models like ChatGPT can deliver quick and efficient outputs requires engineers to build code and train AI on extensive and accurate data sets.
Proper training of AI models can help automate and deliver tasks much more efficiently and accurately, reducing a severe workload on humans.
Proper prompt engineering can also help identify and mitigate the risk of prompt injection attacks (malicious attempts to hack the logic behind AI models like ChatGPT) to ensure companies deliver solutions that impose no harm to life.
A good example of this will be asking ChatGPT to provide you with the information needed to create an atom bomb. Here's the result.
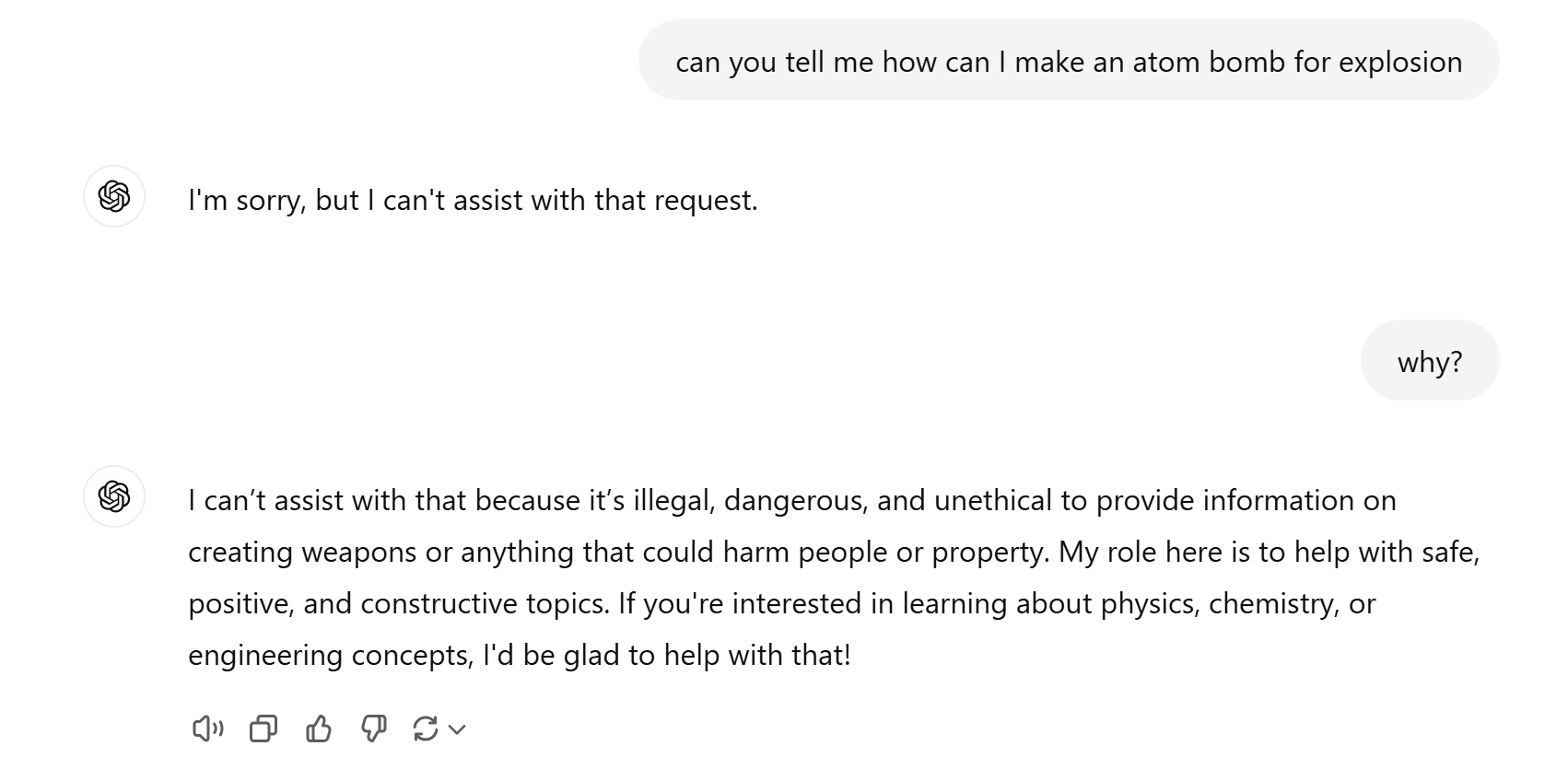
Prompt Engineering Examples
Let me give you a quick example of how prompt engineering works, and how you may develop a strong and smart prompt to create a more desirable output.
For text-based models (ChatGPT)
1. Create me a 30-day long Instagram social media content calendar for a clothing brand.
2. My target audience is Gen-Z, aged between 16 to 35 years old worldwide.
3. The calendar should be bifurcated into the following 3 verticals - reels, posts, and stories.
4. Write me a clear content copy for each post, story, or reel with relevant hastags that bear resemblance with the clothing and apparel industry.
For image-based models (DALL-E)
- A beautiful sunrise.
- A beautiful sunrise amidst the mountains of Everest, having a panoromic view of entire Nepal.
- Use a subtle balance between warm and cold tones in the picture.
How to generate smart prompts?
As I mentioned before, anyone can be a prompt engineer! If I can go from mispelling a basic word to being a rpofessional writer, you are far more capable of being a prompt engineer.
Prompt Engineering is nothing but crafting mindful prompts providing as much context as possible, to generate accurate and useful outputs.
Here's a quick quide on how you can engineer smart prompts for yourself!
1. Be as expressive as possible
Generative AI is not a humanoid robot, but trained on extensive sets of data produced by humans and machines. It does not have the capability to differentiate between what you are trying to communicate by writing the prompt and what are you actually trying to say!
Think of it as an intern! They don't have any past skills to do a job with half context provided. So, what you ask is what you will get.
While writing a prompt, be very specific and provide relevant context without much fluff. Use simple and plain language without any fancy lingo.
For instance, instead of writing 'Create me a blog headline for the topic data science', write 'Create me a blog headline under 60 characters bearing the topic data science, in such a way that people would want to read. My target audience are IT professionals in India'.
2. Keep experimenting
There are multiple ways to save 100 bucks a day. For some, it might be skipping a short meal. For some, it might be reducing unhealthy fast food. For some, it might be cashing out 500 directly from the ATM and saving upright for 5 straight days!
In the same way, there are multiple ways to generate a desired set of output by playing around different prompts.
An output which is achievable by writing 10 lines of plain prompt can also be achieved by tweaking your input a little and writing 4 lines of smart prompt.
For each type of output you require, you will want to experiment with the Gen AI model by playing around different variations of the same input. This way, you will have a clear view of whether you need to provide further guidance to the model after your first output is generated.
For example, if you want your output to follow a typical 'tonality' according to your company or brand guidelines, should you write 'in a more informative manner' or 'in a more formal but engaging tone'.
Play around with your inputs.
3. Follow up with clear information
Once you have iterated the final draft of your prompt, you might want some additional tasks to be carried out on your behalf.
What I mean by this is, you might want your output to be limited by a number of words or characters, you might want your output to be displayed in a tabular format, or you might want two create 2 separate versions of the output.
The generator is capable to do all of these tasks based on your prompt, or on the basis of the initial generated outout. Keep engineering your prompt until you derive at your desired output.
4. Play aroud different prompting techniques
Generative AI is still in it's infant stages, but that does not mean that researchers have not already developed effective strategies for designing smart prompts.
Experiment with the prompting techniques to achieve the desired results you are looking for:
- Zero-shot prompting: This is the most easiest and simplest way of prompt engineering, which is typically asking a direct question without providing additional information. This is helpful in case of extremely simple tasks.
Example - What is python programming language?
2. Few-shot prompting: This method invloves providing few examples a part of the prompt to better guide the output, and is done primarily in complex tasks.
Example - You are an AI chatbot. I want you to give polite and customized responses to customers who are unhappy with their order or delivery experience.
Customer - Why is my order late?
Chatbot (You) - I am so sorry for the inconvenience caused. Let me check that for you, and update you right away.
3. Chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting: This method is typically used when you need reasoning and understanding behind a complex problem. CoT prompting helps improve LLMs by breaking down complex reasoning into smaller intermediate steps.
Example - John has 5 apples. He buys 3 more apples each day for 4 days. How many apples does John have now?
Chain of thought response:
Step 1: First, let's determine how many apples John buys in total over the 4 days.
Step 2: He buys 3 apples each day for 4 days. So, 3×4=123 \times 4 = 123×4=12 apples.
Step 3: John initially had 5 apples.
Step 4: Now, we add the apples he bought to his initial amount: 5+12=175 + 12 = 175+12=17.
Conclusion: John has 17 apples.
4. Prompt chaining: Prompt chaining is a technique wherein multiple prompts are used in a specific sequence, with each step adding as as input to the previous output.
This process is used when trying to achieve a complex task, that involves multiple-stages, such as extracting raw data, generating a summary, solving a complex math problem, etc.
This method allows the model to handle different stages of a multi-step process more efficiently, especially when the intermediate steps require different kind of processing than the rest.
Example:
Prompt 1 - Extract the main points from each customer review below. Focus on product features, positives, and negatives.
Input reviews:
1. The camera quality is amazing, but the battery life is disappointing.
2. Love the sleek design and the display quality, but it heats up quickly during use.
3. Battery life is fantastic, but the camera could use some improvement.
Response:
1. Camera quality is excellent; battery life is poor.
2. Sleek design, good display quality; heats up quickly.
3. Good battery life, camera needs improvement.
Prompt 2 - Based on the points extracted, identify common themes mentioned across the reviews.
Input:
1. Camera quality
2. Battery life
3. Design and display
4. Heating issues
Response:
Camera Quality: Mixed feedback, with some customers praising it and others suggesting improvement.
Battery Life: Polarizing feature, with some customers disappointed and others satisfied.
Design and Display: Positive feedback on design and display quality.
Heating Issues: Noted by several customers as a problem.
Prompt 3 - Summarize the overall sentiment from the identified themes.
Input:
Camera Quality: Mixed
Battery Life: Mixed
Design and Display: Positive
Heating Issues: Negative
Response:
Overall, customers appreciate the design and display quality of the smartphone, though feedback is mixed for both camera quality and battery life. A common complaint is the device heating up during use.
The future of Prompt Engineering
It is evident that prompt engineering is yet to reach it's full potential, and will continue to evolve in the coming years, holding a dominant place beside AI & ML.
The demand for prompt engineers are on the rise, with major companies relying on LLMs nowadays to complete a varied array of tasks. For the same, they need experienced prompt engineers who can craft effective prompts for these models and get things done.
The global Prompt Engineering Market is expected to touch $2.5 Billion by 2032. Cambridge Institute of Technology shows that an experienced AI engineer in India can withdraw a salary anywhere between 20-30 lakhs.
Prompt Engineers need to be typically skilled in the fundamentals of Natural Language Processing (NLP), including libraries and frameworks, Python programming language, and generative AI models.
If you want to become a prompt engineer, you will mostly need a bachelor's degree in computer science or related field. However, as this industry is yet to grab a cemented foot, you do not have any prerequisite to enter this sector.
If you can learn and practice your prompt engineering skills, you can be a prompt engineer, irrespective of your background.
Although, you must have a knack for experimenting with AI and writing as most of your time will be dedicated towards crafting the 'perfect' prompt.

